Search Results
Results for: 'Key Molecules at Metabolic Crossroads'
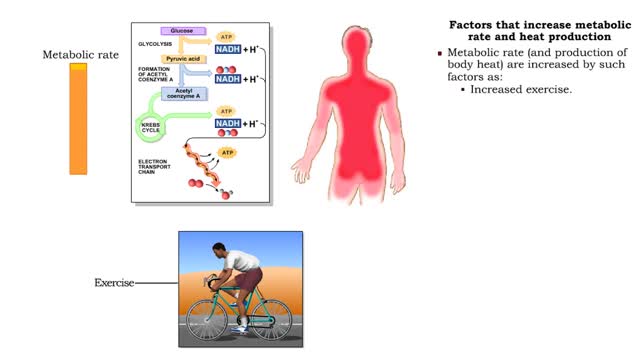
Factors that increase metabolic rate and heat production
By: HWC, Views: 6648
• All vital biochemical reactions are temperature dependent. • The overall rate at which metabolic reactions use energy is known as the metabolic rate. • Metabolic rate greatly determines body temperatures. • Temperature is maintained by balancing the loss of heat to the environment...
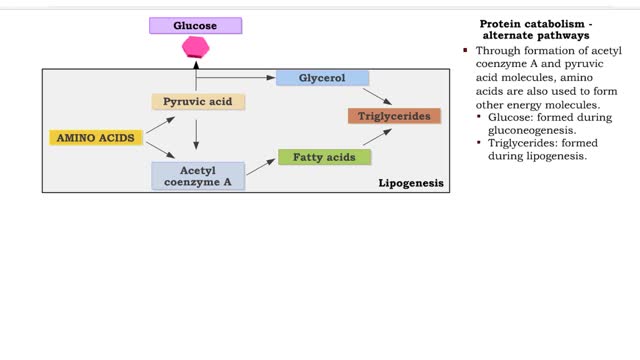
Protein catabolism (Krebs cycle) and Protein anabolism (protein synthesis)
By: HWC, Views: 7022
• Deaminated acids are brought into the Krebs cycle to be oxidized to CO2 and H2O. • Before entering the Krebs cycle, the deaminated acids are converted into intermediate products (pyruvic acid, acetyl coenzyme A, carbonic acids). • In the Krebs cycle, amino acids are oxidized to form r...
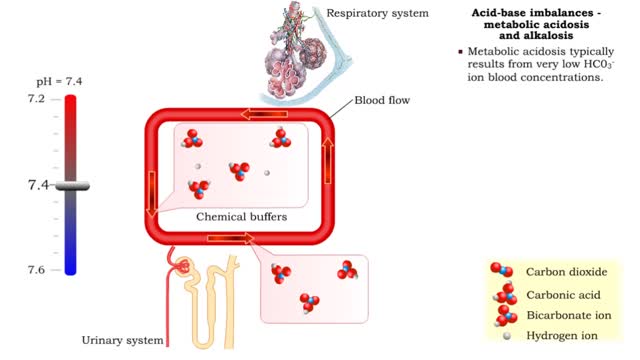
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 6691
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
By: HWC, Views: 6213
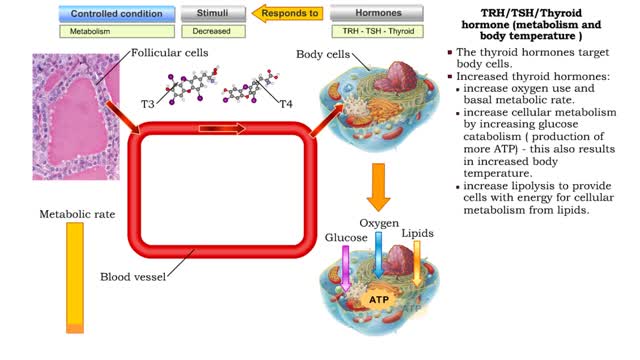
Thyroid hormone production • A decline in metabolic rate caused by increased metabolic need or physical exertion stimulates the production of thyrotropin hormone releasing (TRH) hormone from the cells of the hypothalamus. • Thyrotropin hormone releasing hormone targets the thyrotrophic ce...
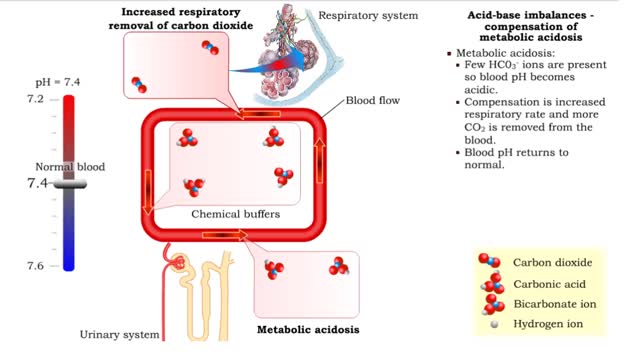
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 6916
1. Metabolic acidosis: • Few HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased respiratory rate and more CO2 is removed from the blood. • Blood pH returns to normal. 2. Metabolic alkalosis: • Many HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes alkaline...
By: HWC, Views: 6796
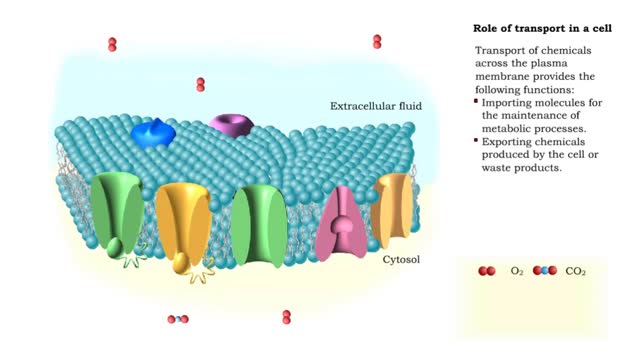
Transport of chemicals across the plasma membrane provides the following functions: Importing molecules for the maintenance of metabolic processes. Exporting chemicals produced by the cell or waste products. Communicating with other cells, allowing for the generation and conduction of a...
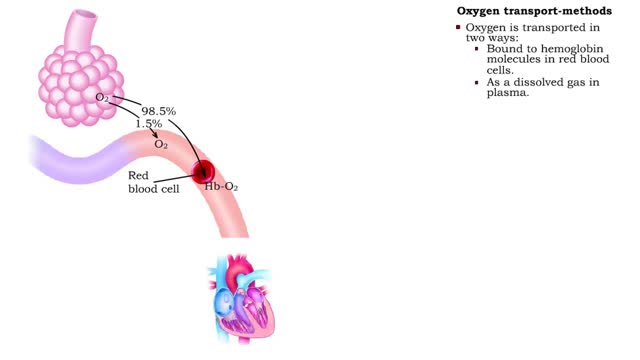
Oxygen transport - methods and oxyhemoglobin
By: HWC, Views: 6412
• The blood is the medium used for gas transport throughout the body. • Oxygen is only available in the lungs. Because the partial pressure of oxygen is higher in the alveoli than in the blood, oxygen diffuses into the blood and is transported to systemic cells. • At the tissues the par...
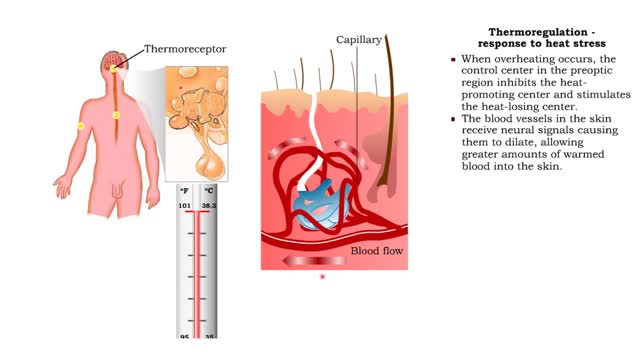
Metabolic Rate, Heat and Thermoregulation - response to heat and cold stresses
By: HWC, Views: 6856
• A neuron group in the anterior portion of the hypothalamus controls heat balance. • Neurons in the preoptic region of the hypothalamus integrate signals that come from thermoreceptors. • The temperature control center in the preoptic region propagates control signals to two other part...
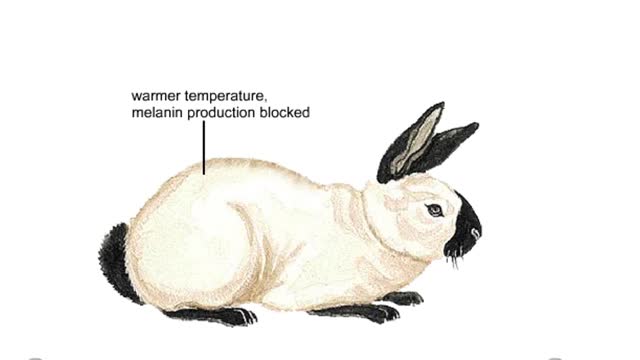
Effect of the environment on coat color in the Himalayan rabbit Animation
By: HWC, Views: 2234
An organism's phenotype—the combination of traits that we observe—is the product of interactions between its genotype and the environment. For example. a Himalayan rabbit is completely white at birth. But within weeks, the fur on the rabbits ears, nose, tail. and lower legs darkens. The...
Advertisement